Managing calf scours ( 1 )
Calf diarrhea or scour can be caused by a range of pathogens. Diarrhea can occur when the ability of the gut to absorb fluids becomes compromised. This can lead to rapid fluid loss. This is why quick rehydration is essential in scour treatments.
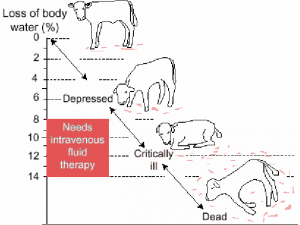
Calves with scour can lose up to 6-10 liters of fluid a day. When appetites are depressed with this fluid loss you can get rapid dehydration.
This is why we advise calves to stay on milk and stay with their mothers (beef). They should receive at least 4 liters of electrolyte solutions in 2 x 2 liter feeds.
Pathogens
The main pathogens can be bacterial, viral or parasitic. Calves under 5-7 days typically can be affected by bacterial agents like ecoli.
Viral scours like rotavirus/coronavirus can affect calves generally from 1-6 weeks of age. With parasites like cryptosporidium and coccidiosis also potentially causing issues
I will dig into both of these in future blogs.
Diagnosis
With scour in calves I think it is important to get a rapid diagnosis of what might be causing the problem. You can use rapid testing kits or get your vet to send a sample to the local laboratory for diagnosis.
A diagnosis as I say “can make a difference”. It will allow you to plan out control measures and may influence treatments.

The cost
Calf diarrheoa the costs?
- While calves and their intestines can recover, their performance can be severely stunted and slowed by this disease
- There is the treatment costs
- In severe outbreaks where colostrum management is poor, it can result in high mortality from calf scour
- Scours open the door to other diseases like pneumonia through the suppression of immunity
- Farmer fatigue, talk to any farmer calf scour is one of the most depressing diseases in a busy calving season
Control
Watch the VIDEO above which explains about control. The thing to remember is calf scour is highly contagious. To isolate any calf showing symptoms quickly to prevent the spread,
Hospital pens with a heat lamp or calf jacket can be very valuable for the sick calf that needs that extra TLC. It also removes the source of infection for other calves.
With groups of calves that become infected then hygiene is critical with feeders and farmers themselves. Some farms will put boarding between pens which may reduce spread.
It is critical that stomach tubes used on sick calves are cleaned and thoroughly disinfected between calves. Have a separate tube for colostrum feeding on the farm.
It is always good practice to limit visitors also to your calf shed and have a very visible (fresh) disinfectant point active on entry to the shed.
Treatments
Speak to your own vet about farm-specific treatment protocols and SOPs you could use. Rehydration is critical with well-balanced electrolyte solutions.
These are really important as they will balance the electrolyte losses and acid-base imbalances caused by scours. Calves once treated early should not require antibiotics, especially oral antibiotics. Having a diagnosis and working with your vet will determine the best action around treatment plans.
Intravenous fluids work really well where fluid loss is severe.
The main elements of calf scour control on-farm should be
- Good colostrum management, quality, quantity and quickly. One area for both beef and dairy calves is also hygiene. Colostrum is the perfect medium for bacterial growth and this can really influence colostrum absorption. For beef cows, this means keeping dry cows on a clean bed to keep udders clean at calving time
- Vaccination plays a role also in reducing the risk of scour. Cows vaccinated before calving will pass the antibodies to the newborn in colostrum. Scour vaccines include rotavirus, coronavirus, and ecoli in them.
- Good hygiene is really critical in reducing the risk and controlling the spread. Deep dry beds with good drainage in well-ventilated sheds.
- Keep feeding calves milk with scour as it keeps energy and hydration up. It also helps the damaged gut heal and repair quicker
- Where issues occur with suckler cows and calves early turnout helps if weather permitting. With dairy calves snatch calving also helps to reduce or limit exposure to the bugs.
This article is just an overview of calf sour, but focus on colostrum, hygiene, early treatment and vaccination
Thought for the day
In challenging times it always good to practice a little bit of gratitude. No matter how difficult the circumstances it can be a good way of gaining perspective. So when the pressure is on take a deep breath, think about everything you have. Its always a good starting point and a good place to keep grounded in.
Big thanks to nettex for their support in helping me make #50in50 happen http://www.net-tex.co.uk
Happy safe farming